The ACEA (European Automobile Manufacturers Association) standards for engine oils are a set of specifications used to define the performance requirements for motor oils in Europe. These standards focus on the protection and performance of engines, including factors like fuel economy, wear protection, and emissions control. The ACEA standards are primarily used in passenger cars, light commercial vehicles, and some heavy-duty diesel applications.
These ACEA standards ensure that the oils meet the specific requirements for engine protection, fuel efficiency, and emission control, based on the type of engine and emission system.
Here is an overview of the main ACEA oil standards:
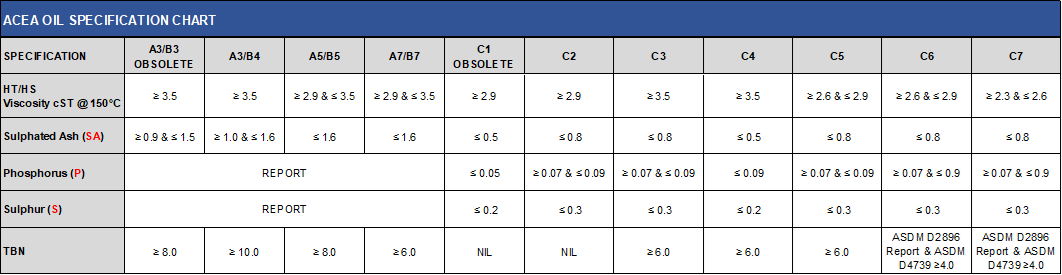
Summary Table:
| ACEA Standard | Type | Key Use | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACEA A1/B1 | Low viscosity, fuel-efficient oils | Older gasoline and diesel engines | Fuel economy, lower viscosity, older engines |
| ACEA A3/B3, A3/B4 | High-performance oils | High-performance gasoline and diesel engines | Excellent wear protection, high-temperature stability, suitable for direct injection engines |
| ACEA A5/B5 | Fuel-efficient, low viscosity oils | Modern gasoline and diesel engines | High fuel economy, low oil consumption, good protection |
| ACEA C1 | Low SAPS oils | Advanced emission control systems, low SAPS requirement | Protects DPF, low sulfated ash, phosphorus, and sulfur content |
| ACEA C2 | Low SAPS oils | Modern vehicles with emission control systems | Moderate low SAPS for emission control, good performance at high temperatures |
| ACEA C3 | Low SAPS oils | High-performance gasoline and diesel engines with emission systems | Better protection, improved performance in high temperatures |
| ACEA C4 | Low SAPS oils | Diesel engines with emission control devices (e.g., DPF) | Very low SAPS content, protects advanced emission systems |
| ACEA C6 | Low viscosity, fuel-efficient oils | Diesel engines with emission systems | Fuel efficiency, LSPI protection, low viscosity |
| ACEA E4 | Heavy-duty diesel oils | High-performance commercial diesel engines | High oxidation resistance, extended oil change intervals |
| ACEA E6 | Heavy-duty diesel oils | Modern commercial diesel engines | Low SAPS content, protects emission systems |
| ACEA E7 | Heavy-duty diesel oils | Older and newer commercial diesel engines | Good wear protection, long oil life |
| ACEA E9 | Heavy-duty diesel oils | Advanced commercial diesel engines | Protects against soot, wear, deposits, improves fuel efficiency |
Low SAPS oil, also known as low-ash oil, is an engine oil that has low levels of sulphated ash (SA), phosphorus (P), and sulfur (S):
1. ACEA A/B Standards (Passenger Cars and Light Duty Vehicles)
- ACEA A3/B3, A3/B4:
- Use: These oils are for high-performance gasoline and diesel engines in cars and light-duty vehicles.
- Key Features: Excellent wear protection, enhanced high-temperature performance, and stability.
- A3: For gasoline engines.
- B3: For diesel engines without a particulate filter.
- B4: For direct injection diesel engines.
- ACEA A5/B5:
- Use: Designed for high fuel economy with low viscosity and optimized for modern engines.
- Key Features: Improved fuel economy and low oil consumption, while still offering good protection.
- A5: Gasoline engines.
- B5: Diesel engines.
- ACEA A1/B1:
- Use: Lower viscosity oils intended for fuel economy in gasoline and diesel engines.
- Key Features: Fuel-efficient and designed for older engine types with low-performance demands.
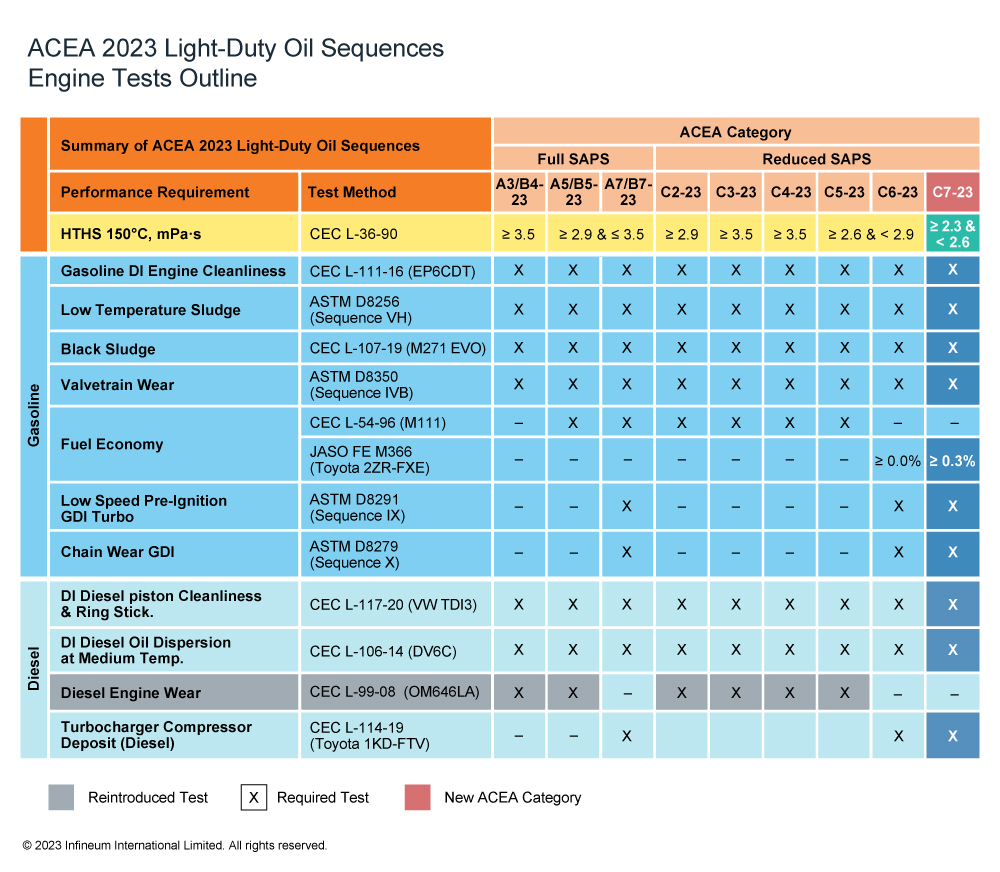
2. ACEA C Standards (Low SAPS Oils)
These oils are designed for modern engines, especially those with advanced emission control technologies like particulate filters (DPF) and selective catalytic reduction (SCR) systems.
- ACEA C1:
- Use: Low SAPS oils for vehicles with advanced emission control systems.
- Key Features: Very low sulfated ash, phosphorus, and sulfur content, helping protect the DPF and ensure longer engine life.
- ACEA C2:
- Use: Similar to C1 but suitable for higher-performance applications.
- Key Features: Moderate low SAPS content for cars with emission control systems.
- ACEA C3:
- Use: Designed for high-performance gasoline and diesel engines with emission systems.
- Key Features: Enhanced protection and better performance in high temperatures, with moderate SAPS content.
- ACEA C4:
- Use: Low SAPS oils for diesel engines with emission control devices (e.g., DPF).
- Key Features: Very low SAPS content for advanced emission systems in diesel engines.
- ACEA C6:
- Use: Developed for low viscosity oils with high fuel economy, particularly in diesel engines.
- Key Features: Improved low-speed pre-ignition (LSPI) protection and optimal fuel efficiency.
3. ACEA E Standards (Heavy Duty Diesel Engines)
- ACEA E4:
- Use: For high-performance diesel engines in commercial vehicles.
- Key Features: High resistance to oxidation and high-temperature stability for extended oil change intervals.
- ACEA E6:
- Use: Heavy-duty diesel engines that require high-performance oils.
- Key Features: Low SAPS oils to protect emission systems in modern heavy-duty diesel engines.
- ACEA E7:
- Use: For older and newer diesel engines in commercial vehicles.
- Key Features: Good wear protection and long oil life.
- ACEA E9:
- Use: Advanced heavy-duty diesel engines that require oils with improved protection for emission systems.
- Key Features: Protection against soot, wear, and deposit formation, along with improved fuel efficiency.
acea c2 vs c3
ACEA C2 and ACEA C3 are both engine oil specifications that are stable and stay in grade, but they have different uses and properties:
ACEA C2
Designed for passenger cars and light duty gasoline and diesel engines, ACEA C2 oils are suitable for extended oil drain intervals. They are low friction and low viscosity, and are compatible with aftertreatment systems. ACEA C2 oils are similar to ACEA C1 oils, but have a slightly higher SAPS limit.
ACEA C3
Designed for modern light duty diesel and high performance gasoline engines, ACEA C3 oils are suitable for vehicles with three way catalysts (TWC) and diesel particulate filters (DPF). They are stable, stay-in-grade oils with a mid SAPS level. ACEA C3 oils have a minimum High Temperature/High Shear (HT/HS) viscosity of 3.5 mPa*s.
ACEA C2 and ACEA C3 oils have similar chemical limits, but different HT/HS figures. A lower HT/HS number provides better fuel economy, but it may not provide the same protection levels.
ACEA oil sequences are designated by a two-part code, with a letter to define the class and a number to define the category. For example, ACEA C2 is a class C oil with a category of 2.
C2/C3 oils are specifically designed to be low-SAPS (sulfated ash, phosphorus, and sulfur) to prevent clogging of DPFs (diesel particulate filters), while A3/B4 oils can have higher SAPS levels and may not be as suitable for such systems; generally, A3/B4 oils might offer slightly better engine protection in certain situations, but may not be as fuel-efficient as C2/C3 oils.
What does ACEA A3 B4 mean?
A3/B4 oils are used in high-performance and direct-injection diesel engines. They can also be used instead of A3/B3-grade oils. A5/B5 oils are low-friction, low-viscosity oils with a high temperature/high shear rate viscosity.